What is ‘healthy soil’?
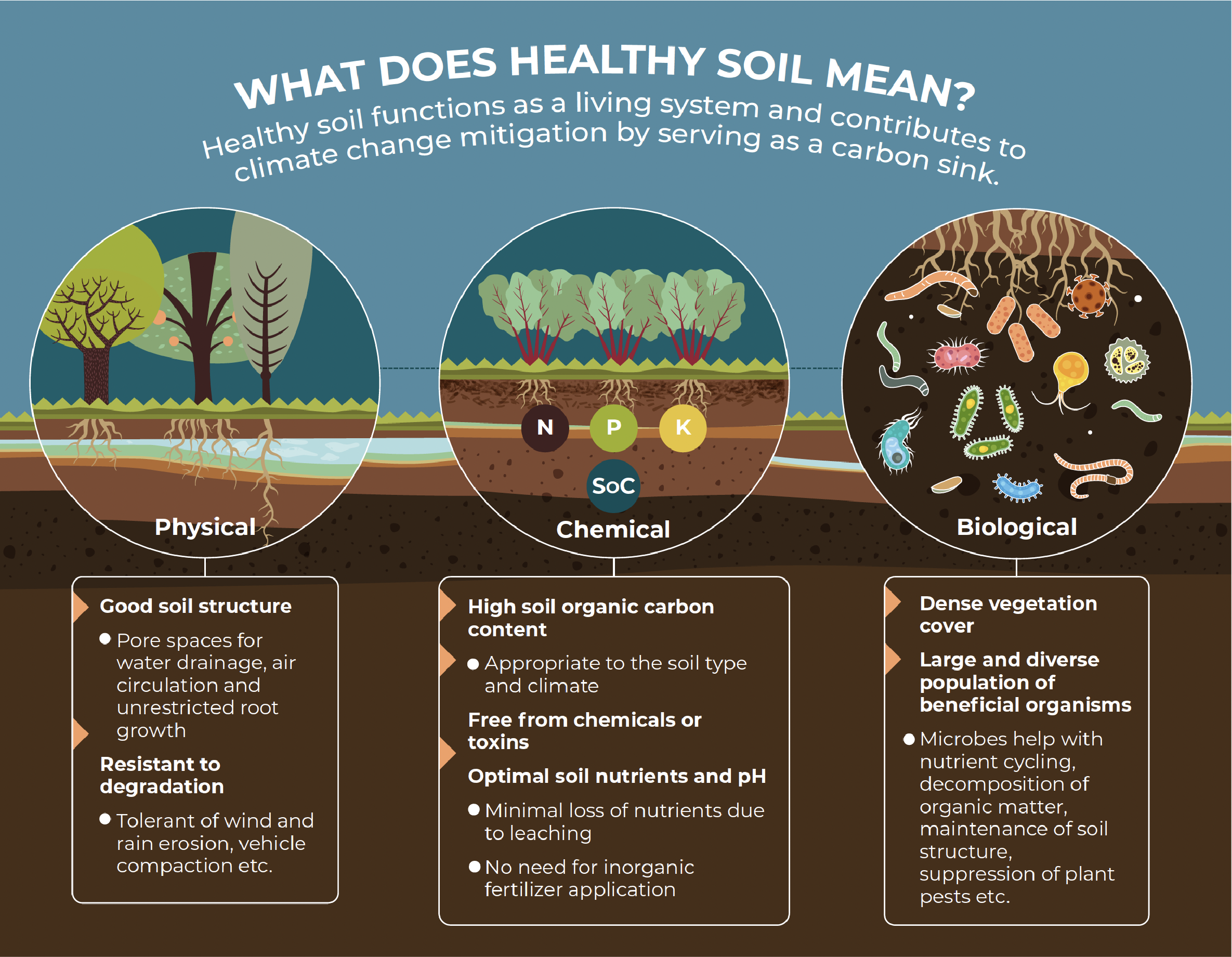
Soil health is the ability of soil to sustain the productivity, diversity, and environmental services of terrestrial ecosystems9. Healthy soil functions as a living system and contributes to climate change mitigation by acting as a carbon sink.
Soil health encompasses the physical, biological, and chemical properties of soil. The chemical properties of soil can be improved by reducing nutrient deficiencies, the accumulation of pesticide residues, and by increasing the soil organic carbon (SOC) content.
Organic carbon content is a key criterion for evaluating soil health. The physical health of soils, its structure and resistance to erosion or compaction, is determined by meteorological factors (e.g. precipitation and wind), the state of soil moisture, and activities such as tillage, the type of cropping system, the application of organic fertilizers and vegetation cover. Healthy soil contains a large and diverse population of soil fauna comprising bacteria, fungi, and invertebrates such as earthworms, mites, collembolans, and nematodes. These organisms assist with nutrient cycling, the decomposition of organic matter and the maintenance of soil structure, amongst other benefits.